prehistoric culture

[prehistoric culture] [cultural/historic
park]
[unique plantlife] [archeological characteristics]
[cultural
history]
[archeological discoveries ]
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
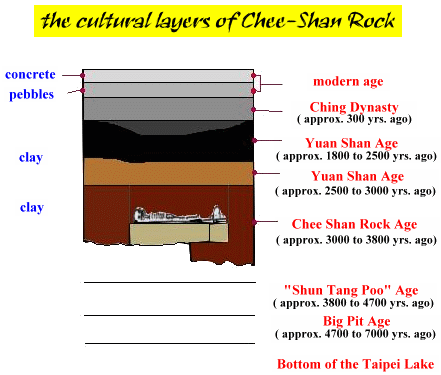
The relics of Chee-Shan Rock included not only the hilltop of Chee-Chung Rd. and Yu-Shen Rd. but also extends downward. From the artifacts that we find, we can see that the cultural layers of Chee-Shan Rock are as follows: old stone age/large pit age/Chee-Shan Rock age/Yuan-Shan age/plant garden age, and the largest being the Yuan-Shan age.
Old stone age
Archeologists have found a stone-made tool that can be used by hand. Judging from the fact that sea animal shells and traces of the tool being immersed in seawater,we suspect that it was thrown away by people at that time. And because there were very few of them, we conclude that they did not permanently reside there.
Big pit age
This age was about 4,700 to 7,000 years ago. These people lived in the big pit in Taipei prefecture, and when the water slowly dried out, they moved to Chee-Shan Rock along the Tun-Shui River. They are a small clan, and used mostly ceramics and few stone products.
Chee-Shan Rock age
Chee-Shan Rock age took place about 3,800 to 3,000 years ago. So far, it has only been found in Chee-Shan Rock, but the artifacts are magnificently diverse, with ceramics, stones, bones, wood, grass, seeds, human bones, fish bones, and shells. In addition, evidence of their ability to cook rice was also found.
Yuan Shan Age
The Yuan Shan age took place around 4,400 to 2,500 years ago. Its most distinguishable characteristic is the discovery of numerous shell tombs, which preserved shells, fish bones, animal bones, and other foods. The recent ( Nov.30, 2000 ) discovery of the two human skeleton in Chee-Shan Rock are from this age.
Plant garden Age
The plant garden age took place about 3,000 to 2,000 years ago. They are the latest period of the new stone age, and the artifacts consists mostly of farming tools. This proves that they relied heavily on farming, and their techniques are much better.
<<interview of the tour guide>>
|
Q : Why are the soil layer of the "plant garden age" black? A : From the layers' color we suspect that the humans then ate barbecued meat, and the coal, when added to the animal fat, would produce this black color; by the same reasoning, we concluded that the humans in the other age ate lots of seafood due to the number of shells that we found. |
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()